Spitzer Space Telescope Captures Galactic Snack
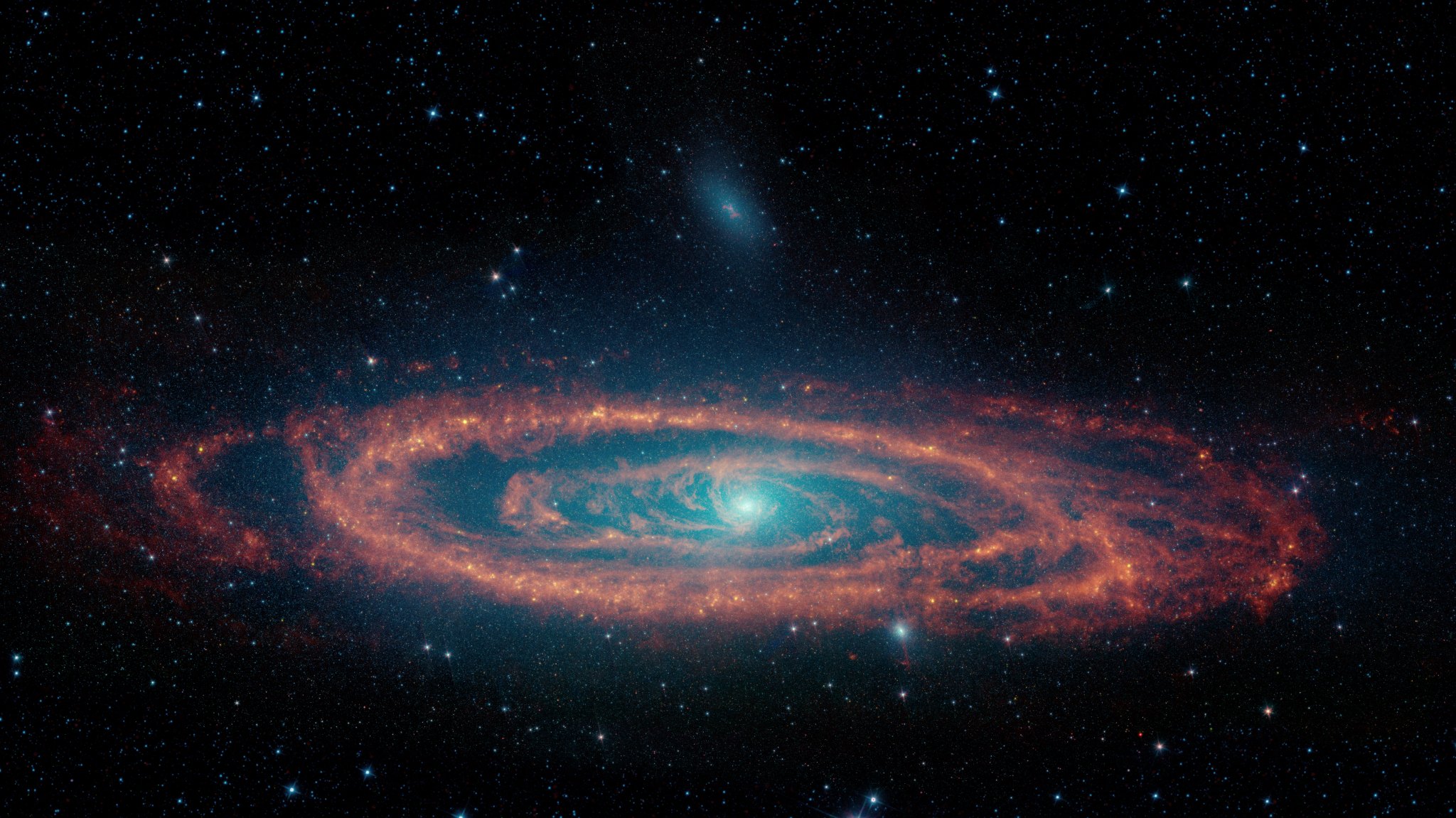
This image, released on May 9, 2024, from NASA’s retired Spitzer Space Telescope shows streams of dust flowing toward the supermassive black hole at the heart of the Andromeda Galaxy. These dust streams can help explain how black holes billions of times the mass of our Sun can satiate their big appetites but remain “quiet” […]

This image, released on May 9, 2024, from NASA’s retired Spitzer Space Telescope shows streams of dust flowing toward the supermassive black hole at the heart of the Andromeda Galaxy. These dust streams can help explain how black holes billions of times the mass of our Sun can satiate their big appetites but remain “quiet” eaters.
Image Credit: NASA-JPL/Caltech